Precision 3D printing with engineering materials
How FDM technology works
Advanced additive manufacturing for prototypes and functional components
FDM (fused deposition modeling) technology, also known as FFF (fused filament fabrication), uses a thermoplastic filament that is extruded through a heated nozzle and deposited layer by layer to create the final component. This method makes it possible to reduce material waste compared to traditional processes and allows you to customize the internal filling of the pieces, optimizing weight, density and strength. However, production times can be longer depending on the geometric complexity of the parts.
Principles of operation
FDM technology operates on a layered additive manufacturing principle, in which the thermoplastic polymer material is heated to its glass transition temperature and extruded through a controlled nozzle. The material is deposited with a programmed motion on a Cartesian plane, allowing the creation of complex geometries by sequential superimposition of solidified layers. This process, one of the most widespread in additive manufacturing, guarantees high reproducibility and dimensional control of the final component.
Advantages
The use of FDM technology allows the production of components with high mechanical strength, thanks to the possibility of selecting advanced engineering materials and optimizing internal filling parameters. This process is particularly advantageous for the production of functional prototypes, lightweight structural components and industrial pre-series, while offering excellent efficiency in terms of material use.
Detriments
Despite its potential, FDM technology has some limitations related to the surface quality of the finished product. Some geometries, particularly those made with carbon fiber (CF) reinforced polymers or highly crystalline materials, may exhibit visibility of print layers and an uneven surface finish. In addition, anisotropic mechanical properties can affect the strength of the component based on the print orientation.
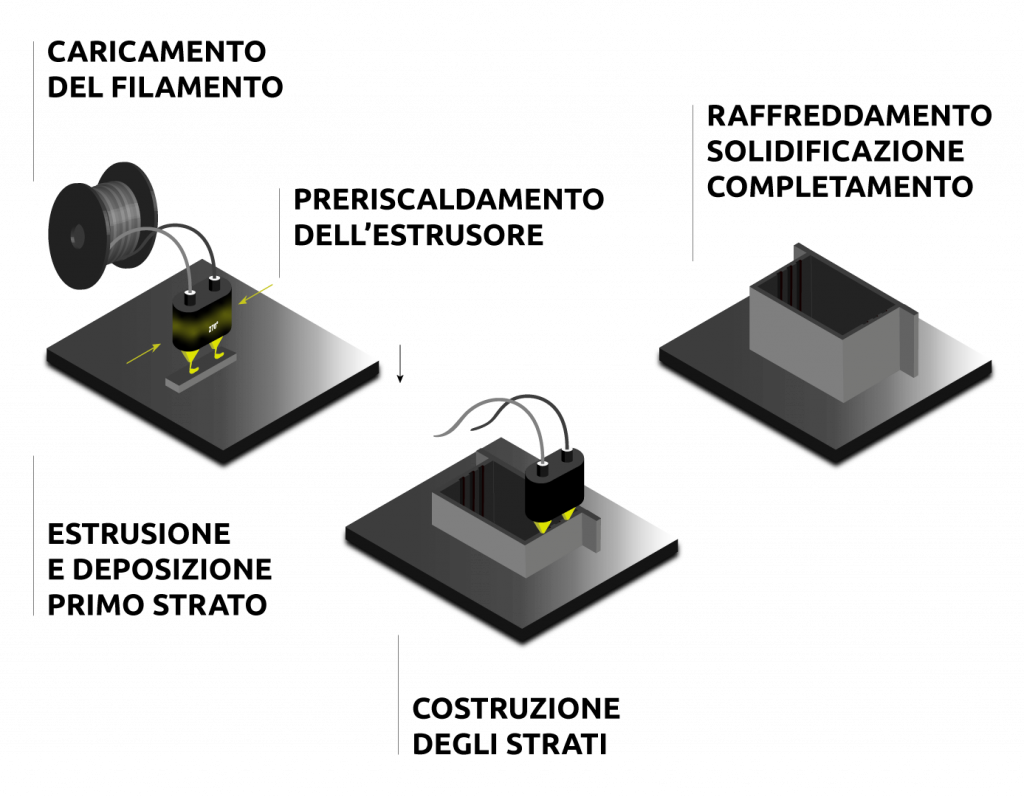
01 - FILAMENT LOADING
A thermoplastic filament is loaded into the printer and fed to the extruder. The material may vary (PLA, ABS, PETG, etc.) depending on the application and customer requests
02 - PREHEATING THE EXTRUDER
The extruder is heated to the melting or filament transition temperature, typically between 180°C and 270°C.
Heating ensures that the filament fuses properly.
03 - EXTRUSION
OF MATERIAL
The extruder pushes the molten filament through a thin nozzle.
The nozzle moves along the paths generated by the slicer, depositing the material layer by layer.
04 - DEPOSITION OF THE FIRST LAYER
The first layer is deposited on the print platform, which can be heated depending on the material used. Heating promotes material adhesion and reduces the risk of warping, ensuring a stable base.
05 - CONSTRUCTION OF THE SUBSEQUENT LAYERS
The print platform lowers one step, corresponding to the thickness of the layer, while the extruder continues to deposit the material, building the object layer by layer. If necessary, support structures are generated simultaneously to ensure the correct realization of the geometries.
06 - COOLING AND SOLIDIFICATION
The thermoplastic cools and solidifies rapidly after deposition. Depending on the type of material, fans can be used to speed up cooling and optimize print quality.
07 - COMPLETION
The process of deposition and solidification of the material continues layer by layer until the object is completely realized, respecting the geometries and design specifications.
08 - POST-PROCESSING (optional)
Once printing is complete, the object is removed from the platform. It can then undergo optional post-processing processes, such as removal of support structures, insert inserts and vapor smoothing.
Optimize your production with FDM technology
Are you ready to optimize your production with reliable and customizable solutions? With FDM technology, we can offer you precise, efficient additive manufacturing suitable for prototypes and small production runs, using a wide range of thermoplastics. Contact us to find out how we can improve the quality, flexibility and cost of your production process.
Why choose FDM technology
FDM 3D printing technology is an ideal choice for those looking for cost-effective, highly customizable, and fast additive manufacturing solutions.
Flexibility
in materials
FDM 3D printing allows you to use a wide range of thermoplastics, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and many others, offering solutions suitable for different application areas, from rapid prototyping to the production of functional components.
Affordable and accessible production
Due to the low need for specialized equipment and the reduction of labor and material costs, FDM technology is a beneficial choice for prototype and short-run production.
High customization and precision
Each part is built layer by layer with great precision, allowing for the creation of complex and customizable geometries, thus responding to the customer’s specific design needs.
Reduced production times
Compared to traditional methods, FDM printing can significantly reduce the time it takes to create prototypes and components, speeding up the product development process and reducing time-to-market.
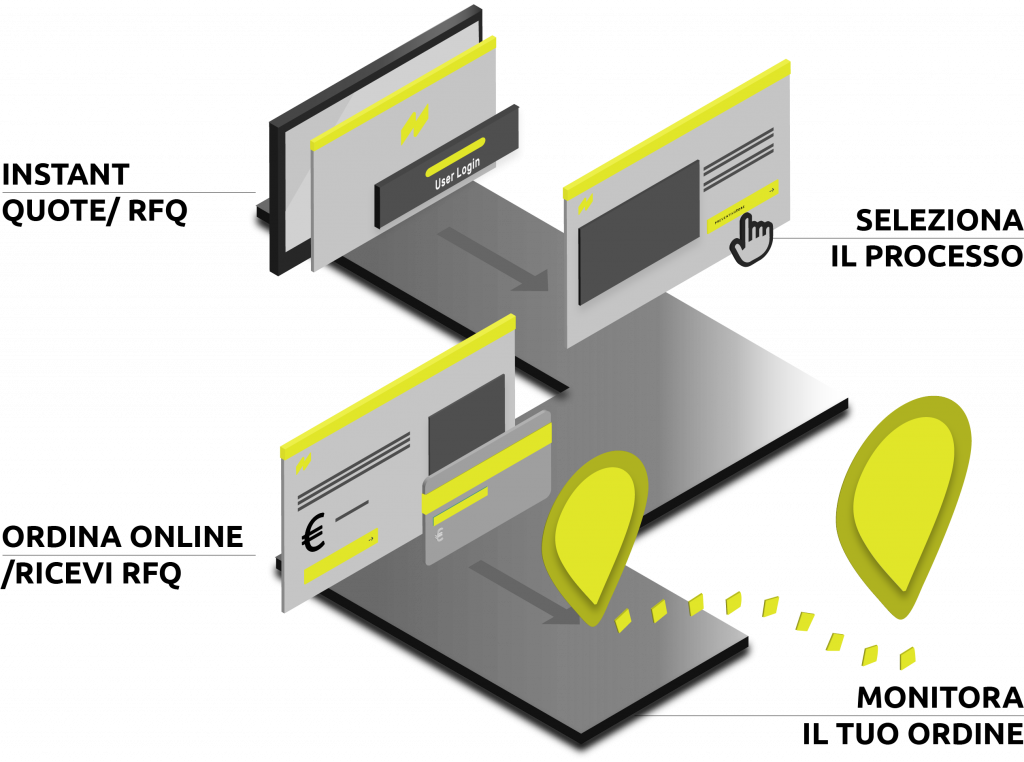
Online quote
Process optimization for competitive production
With our online platform, uploading your files and getting a quote is a matter of a few clicks.
Choose the most suitable technology, configure materials, finishes and every technical detail of your request. Receive a instant quote or a custom RFQ and confirm your order in just a few clicks.
You will be able to monitor the progress in real time directly from your reserved area. A fast, transparent and professional production process, without complications.